In the oil and gas industry, the process of drilling is integral to exploring and extracting valuable resources buried deep beneath the Earth's surface. A crucial component of this drilling operation is the use of Drilling Mud Pumps, which are designed to circulate drilling fluids into the borehole. These pumps play a vital role in maintaining the pressure necessary to prevent collapses, carrying cuttings to the surface, and cooling the drill bit, thereby enhancing efficiency and safety during drilling operations.
Drilling Mud Pumps work by managing the flow of drilling mud, a mixture of water, clay, and other additives that lubricate the drilling process and stabilize the wellbore. The functionality of these pumps relies on their ability to deliver a continuous and controlled flow rate, which is key to effective drilling. As the drilling progresses, the choice and management of the mud are essential—impacting not only the efficiency of resource extraction but also the environmental footprint of the operations.
Understanding the mechanics and importance of Drilling Mud Pumps is essential for professionals in the oil and gas sector. These pumps not only facilitate efficient drilling but also contribute to the overall integrity of the drilling process. Their role in managing pressure and removing cuttings makes them indispensable for successful and safe drilling operations, highlighting the need for ongoing innovation and maintenance in this critical aspect of the industry.

A drilling mud pump is an essential component in oil and gas operations, primarily responsible for circulating drilling fluid, or mud, during the drilling process. The drilling mud serves multiple purposes, including cooling the drill bit, removing cuttings from the borehole, and maintaining pressure to prevent blowouts. The pump ensures that the mud is delivered at a consistent flow rate and pressure, which is crucial for efficient drilling and safety in operations.
Tips: When selecting a drilling mud pump, consider factors such as the type of drilling mud being used and the required flow rate. It's essential to ensure that the pump can handle the viscosity and density of the mud to maintain optimal performance.
The functionality of drilling mud pumps relies on their ability to generate necessary hydraulic pressure. As the pump draws mud from the storage tanks, it pressurizes the fluid and sends it through the drilling assembly and back to the surface. This continuous cycle helps lift the drill cuttings and maintains a stable borehole environment. Understanding the operational mechanics of drilling mud pumps can significantly improve the efficiency of drilling operations.
Tips: Regular maintenance of the pump and its components is critical to avoid downtime. Implementing a routine inspection schedule can help detect potential issues before they lead to costly repairs or delays in the drilling process.
In the oil and gas industry, drilling mud pumps play a crucial role in circulating the drilling fluid, or mud, which is essential for maintaining the stability of the borehole and cooling the drill bit. There are several types of drilling mud pumps utilized in operations, each designed to meet specific needs based on the drilling environment and requirements. The most commonly used pumps include positive displacement pumps, centrifugal pumps, and triplex pumps.
Positive displacement pumps are ideal for high-viscosity muds, as they can generate a consistent flow rate, ensuring efficient circulation even in challenging environments. According to a report by the American Petroleum Institute (API), these pumps are often employed in deepwater drilling operations due to their ability to handle large volumes of heavy drilling fluids. On the other hand, centrifugal pumps are more suitable for less viscous muds and are widely used in land drilling operations due to their lower operational costs. However, they may not perform as effectively under high-pressure conditions.
Triplex pumps, characterized by their three-cylinder design, are gaining popularity for their durability and reliability. They provide an efficient solution for high-pressure pumping needs, making them a preferred choice in various drilling applications. A study by the Society of Petroleum Engineers indicates that the usage of triplex pumps can enhance operational efficiency by approximately 20%, contributing significantly to overall productivity in drilling operations. Understanding the different types of drilling mud pumps and their applications is crucial for optimizing oil and gas extraction processes.
| Pump Type | Working Principle | Application | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Moves fluid using rotational energy from a volute or diffuser. | Common in mud circulation systems. | High flow rates, efficient for large volumes. |
| Positive Displacement Pump | Moves fluid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it out. | Suitable for high viscosity fluids. | Handles thick mud efficiently, consistent flow rate. |
| Triplex Pump | Utilizes three pistons to create pressure and flow. | Used in drilling operations for large bore wells. | Robust construction, reliable and efficient under high pressure. |

A drilling mud pump is essential in oil and gas operations, facilitating the circulation of drilling fluid, also known as mud, through the wellbore. Understanding the key components of a drilling mud pump is crucial for ensuring its efficient performance. One of the primary components is the pump casing, which houses the internal mechanisms and is designed to withstand high pressure. The casing plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the pumping process and preventing leakage.
Another vital component is the pistons or plungers. These parts move within the pump to create suction and pressure, allowing the drilling mud to be drawn in and expelled. The movement of these pistons is synchronized with the reciprocating action of the pump, ensuring a continuous flow of drilling fluid. Additionally, mud valves regulate the entry and exit points of the fluid, ensuring that the proper amount of mud is maintained within the system, thereby optimizing performance and preventing issues such as fluid loss or over-pressurization. Understanding these components and their functions helps in managing the drilling process effectively and maintaining operational efficiency.
Drilling mud pumps play a crucial role in optimizing drilling efficiency and cost-effectiveness in oil and gas operations. These pumps are responsible for circulating drilling fluids—commonly known as drilling mud—through the wellbore and back to the surface, ensuring that the drilling process remains efficient and safe. According to a report by the Society of Petroleum Engineers, an optimal mud system can reduce drilling time by up to 30%, significantly lowering operational costs. The efficiency of drilling mud pumps directly impacts the overall drilling performance, influencing rate of penetration (ROP) and the ability to manage wellbore stability.
Additionally, advancements in drilling technology and pump design have led to more robust and efficient mud pumps that minimize maintenance costs and downtime. For instance, modern pumps are engineered to handle higher pressures and volumes, allowing for better cuttings removal and cooling of the drill bit, thereby enhancing the drilling process. A study conducted by the International Association of Drilling Contractors indicated that the use of advanced mud pumps can contribute to a reduction in non-productive time (NPT) by approximately 15%, translating to significant savings over the course of a drilling project. By leveraging these technologies, operators can maintain effective drilling operations while optimizing their budgets in a highly competitive market.
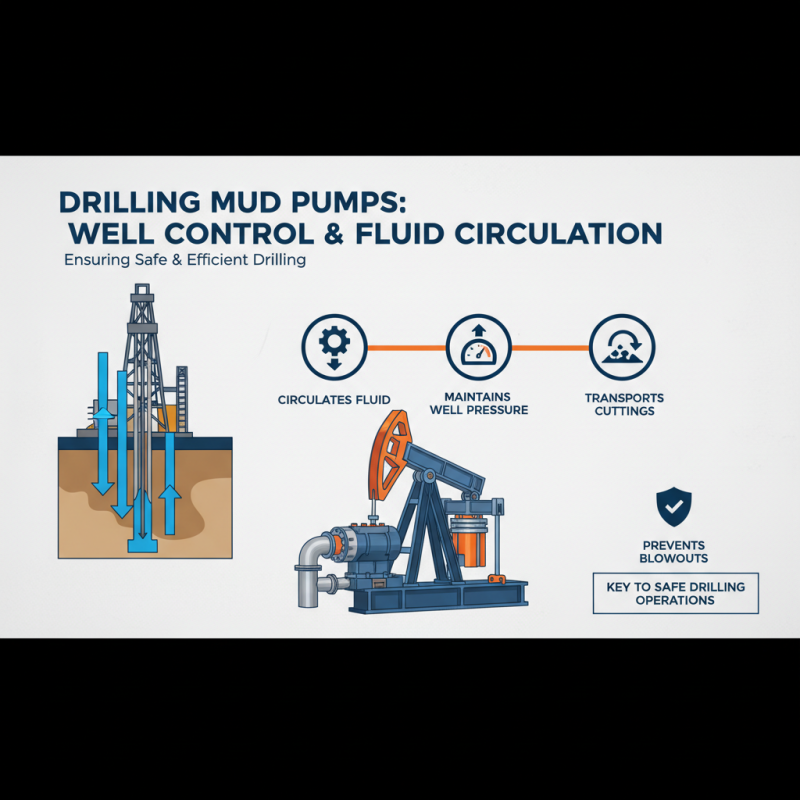
Drilling mud pumps play a crucial role in oil and gas operations by ensuring effective well control and fluid circulation during drilling activities. These pumps are responsible for circulating drilling fluid, also known as mud, down the drill string and back up the annulus. This continuous flow is essential for maintaining well pressure, preventing blowouts, and returning cuttings to the surface for disposal. By managing the pressure balance within the well, drilling mud pumps provide a safe and controlled environment for drilling operations.
In addition to well control, drilling mud pumps facilitate the cooling and lubrication of the drill bit, which is vital for efficient drilling. The mud also serves to stabilize the wellbore, reducing the risk of collapses and other geological hazards. When properly managed, the circulation of drilling fluid helps to remove rock cuttings from the well, keeping the drilling process continuous and minimizing downtime. Thus, drilling mud pumps are indispensable for the efficient operation of drilling rigs, contributing significantly to overall safety and productivity in oil and gas exploration.

